If you’ve thought about building a website and running an online business, securing your data is non-negotiable. You can’t rest easy knowing your precious data is out there, accessible to many, and potentially at risk. But don’t panic—this is where a good SSL certificate comes into play, encrypting your data and keeping it safe. Not sure what that means? In simple terms, it’s like an “identity card” for your website. It establishes a secure connection between the user’s browser and the web server. If you’re new to this and unsure how to spot a website with an SSL certificate, here’s a hint: it’s indicated by “https://” and a padlock icon. Pretty interesting, right? Let’s discuss everything you need to know about SSL certificate installation.
What is an SSL Certificate?
An SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificate is a small data file that creates a secure, encrypted connection between a web server and a browser. When you install an SSL certificate on your website’s server, it enables HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) rather than HTTP. This means that all the data exchanged between the website and the browser is encrypted, which makes it incredibly difficult for hackers to intercept or tamper with.
It’s important to note that SSL certificates are used to protect sensitive data. Whether it’s usernames, passwords, credit card information, or personal details, SSL ensures that this information remains private while it’s being transferred over the internet.
Websites with SSL certificates are indicated by the “https” prefix in their URLs and a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar. These symbols reassure users that their data is safe and that they’re interacting with a legitimate website.
Why SSL Certificates are Essential for Your Website
You may think that SSL certificate installation is only important for websites handling sensitive customer data, like e-commerce sites. While that’s definitely a big reason to use SSL, there are several other reasons why SSL is essential for every website.
Security
The main purpose of an SSL certificate is to encrypt data exchanged between the user and the website. This means that information like credit card details, login credentials, and personal data is encrypted, ensuring hackers can’t access or steal that information while it’s being transmitted. Without SSL, this data could be intercepted easily by cybercriminals.
Builds Trust with Your Visitors
Trust is one of the key elements of a successful website. When users see the padlock icon or the HTTPS label, they know their data is protected. This builds confidence in your site, encouraging them to stay longer, browse more, and make purchases without fear of data theft. Websites without SSL certificates, on the other hand, may display a warning in the browser, which can drive visitors away.
SEO Benefits
Search engines like Google prioritize websites that use HTTPS. SSL certificates are a ranking factor, which means that websites with SSL certificates are favored in search rankings over those without. If you’re running a website for business purposes, securing an SSL certificate can give you a small but important SEO advantage. In a competitive online world, every bit counts!
Compliance with Regulations
If your website deals with sensitive information—such as personal data, health information, or financial data—you need to comply with regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard). These regulations often require SSL certificates to ensure that any data transferred from your users is protected. Failure to comply could lead to heavy fines or loss of customer trust.
Prevent Phishing and Impersonation
SSL certificates help protect your website from phishing attacks. When you don’t have SSL, cybercriminals can create fraudulent versions of your website to steal data from unsuspecting visitors. With SSL, the verification process ensures that users are interacting with the real website and not a fraudulent clone designed to steal information.
How SSL Certificates Work

Credit: acclaim.agency
The process behind SSL certificate management is simple yet powerful. Here’s a basic breakdown of how it works when someone visits your website:
Initiation of the Secure Connection
When a user visits your website, their browser checks if the website has an SSL certificate. If it does, the browser establishes a secure, encrypted connection with your server. This is why websites with SSL show “https://” instead of just “http://”.
SSL Handshake
During the SSL handshake, the server and the browser exchange encryption keys. The server sends a copy of its SSL certificate to the browser. The browser then verifies the authenticity of the certificate.
Encryption of Data
Once the certificate is verified, the server and browser create a secure connection where all the data transferred between them is encrypted using public and private keys. This encryption ensures that even if someone intercepts the data, it would be meaningless without the decryption keys.
Authentication
SSL certificates also authenticate the identity of the website, confirming that it’s truly who it claims to be. This is particularly important for websites that handle sensitive user information, like online stores or banking websites.
Types of SSL Certificates

Credit: thesslstore.com
There are different types of SSL certificates, each designed for specific website needs:
Domain Validated (DV) SSL Certificates
Quick and Easy: This is the most basic form of SSL certificate. The provider only verifies domain ownership, making it a fast and cheap option. Ideal for small websites or blogs.
Organization Validated (OV) SSL Certificates
Enhanced Trust: The SSL certificate provider verifies the organization’s identity in addition to domain ownership. This provides more trust for business websites, as visitors can confirm that the website is operated by a verified company.
Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates
Highest Level of Validation: EV certificates require extensive validation and show the website’s organization name in the address bar with a green padlock. This type is recommended for e-commerce sites and other high-traffic, high-trust websites.
Wildcard SSL Certificates
Multi-Subdomain Protection: A wildcard SSL certificate secures your main domain and unlimited subdomains (e.g., blog.yourdomain.com, shop.yourdomain.com) under one certificate.
Multi-Domain SSL Certificates
Multiple Domains Under One Certificate: This SSL certificate secures several different domain names with a single certificate, which is ideal for businesses with multiple websites.
Free vs Paid SSL Certificates
![]()
Credit: eurodns.com
When it comes to SSL certificate management, you have two main options: free or paid. Let’s compare the two.
Free SSL Certificates
- What Are They? Free SSL certificates are typically offered by providers like Let’s Encrypt. These certificates are domain-validated, offering basic encryption without any additional features or verification.
- Pros: They’re completely free, easy to install, and sufficient for small websites or personal blogs.
- Cons: They don’t offer extended validation, warranties, or customer support. Plus, they often expire every 90 days, so you need to renew them frequently.
Paid SSL Certificates
- What Are They? Paid SSL certificates offer different levels of validation (DV, OV, EV) and come with additional features like higher encryption, warranties, and extended support.
- Pros: Paid certificates provide added trust and security, ideal for businesses and e-commerce websites. They typically last 1-2 years and come with dedicated support.
- Cons: They come with a cost, which varies depending on the certificate type and provider.
For businesses and e-commerce websites, it’s generally better to go with a paid SSL certificate for enhanced trust, security, and support.
How to Install an SSL Certificate on Your Website
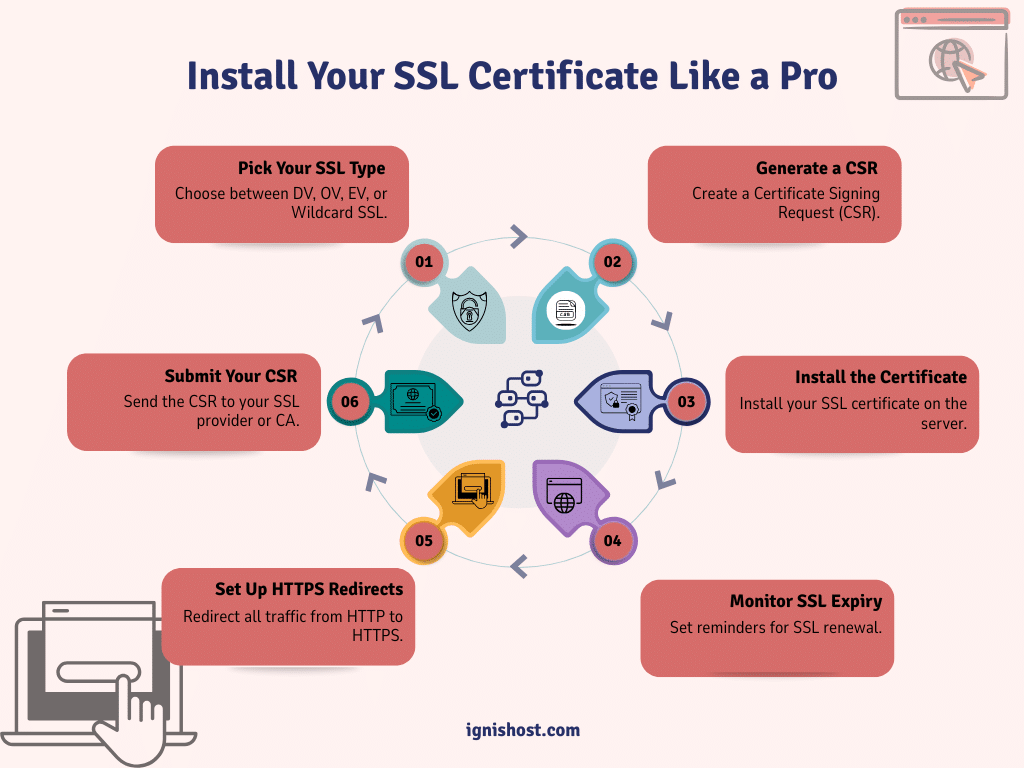
Credit: thesslstore.com
Installing an SSL certificate might sound complicated, but it’s actually a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Purchase or Obtain an SSL Certificate: You can purchase an SSL certificate installation from trusted providers like GoDaddy, DigiCert, or you can use a free certificate from Let’s Encrypt.
- Generate a CSR (Certificate Signing Request): Before installation, you need to generate a CSR, which is a unique code that identifies your server. This can be done in your hosting provider’s cPanel or server control panel.
- Submit the CSR to Your SSL Provider: For the next step, you have to submit your CSR to your chosen certificate authority (CA). They will validate your domain and send you the SSL certificate.
- Install the SSL Certificate: Once you’ve received your SSL certificate, install it on your server. Hosting providers often offer guides for installing the certificate. If you use cPanel, the process is quite simple through the SSL/TLS section.
- Set Up HTTPS Redirects: After installing SSL, set up 301 redirects to ensure all traffic is securely routed to the HTTPS version of your site.
- Test the Installation: Use online tools like SSL Labs’ SSL Test to verify that your SSL certificate is installed correctly.
Common SSL Installation Errors and How to Fix Them
SSL installation not going smoothly? Let’s go over the typical problems and solutions.
Certificate Not Trusted
Ensure that your root and intermediate certificates are correctly installed. If they’re missing, browsers will flag the site as untrusted.
Mixed Content Warnings
If some of your site’s resources (images, scripts) are loaded over HTTP instead of HTTPS, browsers will show warnings. Update all links to HTTPS.
SSL Certificate Expiry
Lastly, you should be aware that SSL certificates typically expire after 1-2 years. Set reminders to renew your certificate before it expires.
Ending Remarks
In a nutshell, installing an SSL certificate is one of the easiest and most important ways to secure your website and protect your visitors’ data. Whether you choose a free SSL certificate for a personal blog or a paid SSL certificate for a business site, the benefits are undeniable. It boosts your SEO rankings, builds trust with users, and keeps sensitive data safe.
So, don’t wait—install an SSL certificate today and start securing your website!
Frequently Asked Questions
Curious about SSL certificates? Let’s address the most common questions.
What is an SSL certificate, and why do I need it?
SSL certificates encrypt data and ensure secure communication between your website and its visitors. They are crucial for building trust and protecting sensitive information.
How do I install an SSL certificate on my website?
The installation involves generating a CSR, purchasing or obtaining an SSL certificate, installing it on your server, and ensuring your site is redirected to HTTPS.
Can I use a free SSL certificate for my business website?
Free SSL certificates are fine for small websites, but businesses, especially e-commerce sites, should consider paid SSL certificates for additional security and validation.
How often do SSL certificates expire?
SSL certificates typically last 1-2 years, so make sure to renew them before they expire.
How do I check if my SSL certificate is installed correctly?
Use tools like SSL Labs’ SSL Test to verify the proper installation of your SSL certificate.




